NMEA 0183 wiring, why it bugs me
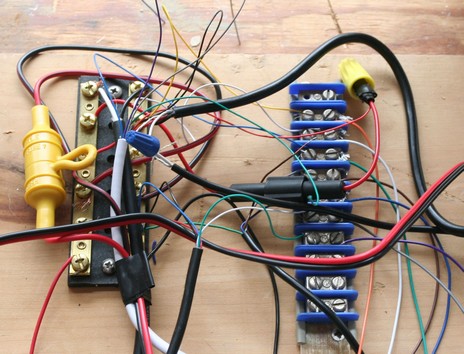
OK, I admit that at least half of the hideous mess above is the fault of yours truly, being sloppy with a temporary install, in this case interfacing a DSC VHF, a GPS, and an AIS receiver all to a Garmin 3210 (possible because it has two 0183 ports, plus a  special Garmin GPS port). But I also blame the standard itself, or non standard really, since there is no common plug, let alone standard wire colors (so you’re delighted to come across nice labelling like Northstar’s at right), or even a uniform nomenclature. Plus the typical bare wires are fine gauge, making them hard to handle and hard to secure strongly. Finally, the variable way the negative side of an 0183 data IN or OUT wire pair works—sometimes wired to its negative OUT/IN opposite, sometimes wired to ground, sometimes not wired to anything—further confuses things, and often means that there’s a partial crossover between the power connection strip (upper left) and the data strip. The photo below, and bigger here, shows how this can all be neatly done, in this case by pros, but it’s still a bit fragile, I think, and it’s going cost you time or money. The chaos and complications of NMEA 0183 wiring make the rugged NMEA 2000 combined data/power cable scheme look very, very good.
special Garmin GPS port). But I also blame the standard itself, or non standard really, since there is no common plug, let alone standard wire colors (so you’re delighted to come across nice labelling like Northstar’s at right), or even a uniform nomenclature. Plus the typical bare wires are fine gauge, making them hard to handle and hard to secure strongly. Finally, the variable way the negative side of an 0183 data IN or OUT wire pair works—sometimes wired to its negative OUT/IN opposite, sometimes wired to ground, sometimes not wired to anything—further confuses things, and often means that there’s a partial crossover between the power connection strip (upper left) and the data strip. The photo below, and bigger here, shows how this can all be neatly done, in this case by pros, but it’s still a bit fragile, I think, and it’s going cost you time or money. The chaos and complications of NMEA 0183 wiring make the rugged NMEA 2000 combined data/power cable scheme look very, very good.


 Share
Share
I completely agree with your observations. It is usually not too difficult to connect the (+) phase outputs to the appropriate inputs, but handling the signal grounds or the (-) phase outputs and inputs can be very confusing. I suspect that some manufacturers have provided unbalanced or single-ended outputs yet have marked the signal ground with a (-), implying a differential output and adding to the confusion of how to properly connect them.
When you add other variables to the interconnection, such as baud rate, it can be come even more frustrating.
My current NMEA-0183 interconnections resemble yours, although slightly neater.